In 1963 GM Design put together two special Corvettes according to special work orders. The first was delivered fresh to the 1963 Chicago Auto show, while a nearly identical version was gifted to the retired Harley Earl. These Vettes received numerous modifications from GM Design including and a new custom interior and sidepipes.
This one-off Corvette was custom-built by GM Styling under famed design chief Bill Mitchell, especially for the famed industrialist and Indianapolis racing sponsor Ozzie Olson of Olsonite fame. Among its special modifications including custom floor grates that were a trademark feature of the GM Styling specials
The most innovative of the Bob McDorman Collection’s GM Styling Corvettes is this Blue Metallic one-off enjoyed by GM Styling legend Bill Mitchell. The unique paint is accented with a custom made die cast front grille and matching dual front fender vents. A willing 327 CI engine gave this gem all the performance the boss could have asked for...
"Bunkie" Knudsen ordered it up in the spring of 1964 for his wife, Florence. This car is as much of a gem today as it was when Florence Knudsen first saw it, so says its current owner, Chevy dealer and noted Corvette collector Bob McDorman. It had custom Pink Pearl paint and custom pink leather interior.
To celebrate the departure of the third-generation Corvette, Chevrolet decided to offer a final commemorative “Collectors Edition” model. However, recalling their experience with the 1978 Pace Car Replicas it was decided that the 1982 Collector Edition Corvettes would be built only “as needed” to satisfy customer orders and that they would get unique vehicle identification plates to help deter someone from turning a standard car into a Collectors Edition knock-off.
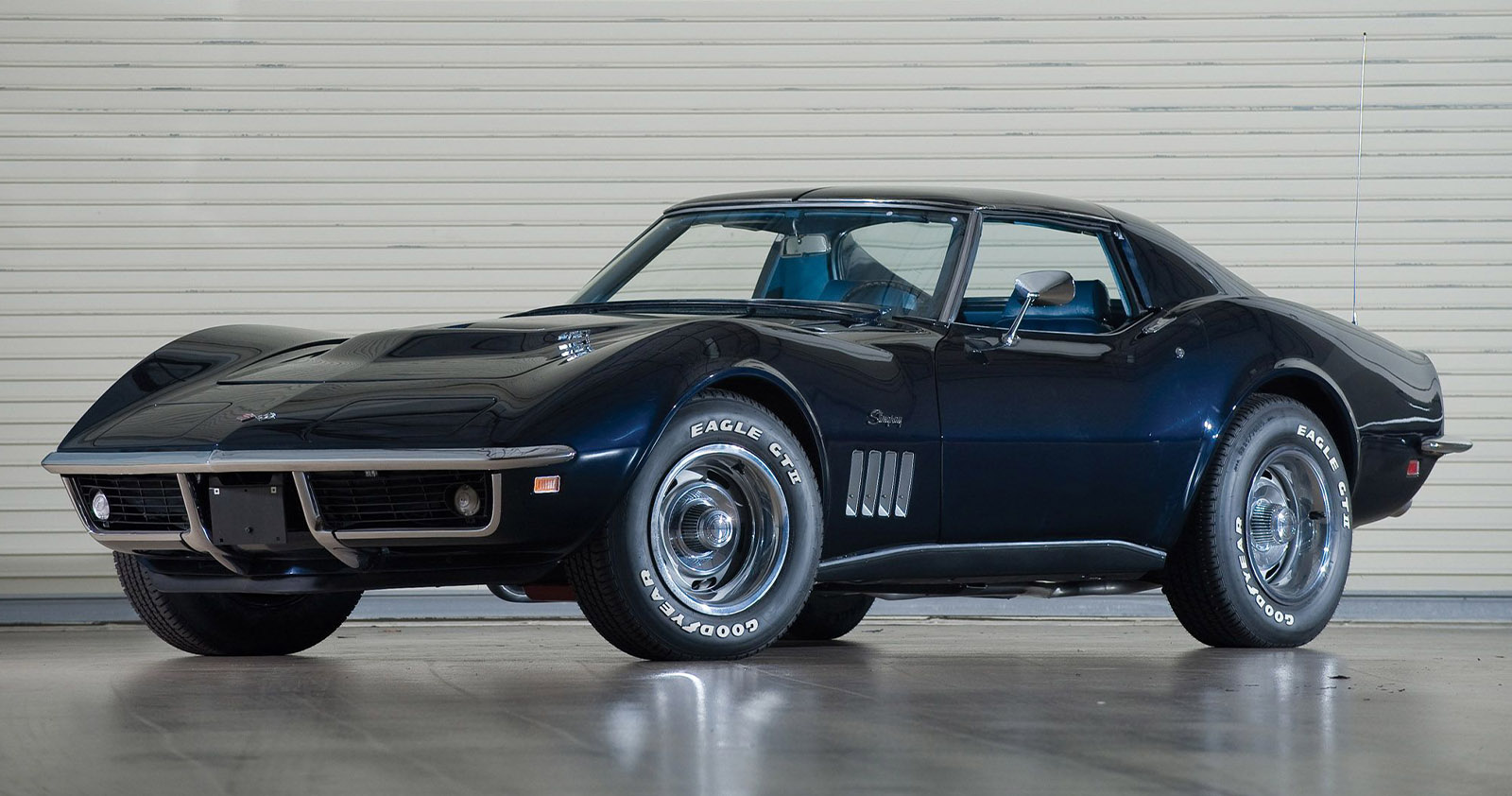
1967 Chevrolet Corvette Sting Ray L89 Tri-Power There were 16 of the 1967 RPO L89 Corvettes manufactured by Chevrolet, thus...
The XP-819, developed in the mid-1960s, was an engineering exercise to test a rear engine concept for the Corvette. The body was designed by Larry Shinoda. You can see styling cues in XP-819 that later appeared in Shinoda's famed "Sting Ray" design. A GM marine engine powers the car so the two-speed transaxle would operate properly. The entire chassis, suspension, and steering are custom made components unique to this car.
The Mako Shark II was a radical concept that shaped Stingray years later. While showcasing distinct design cues, the Mako Shark contained many notable features for 1965. It had a one-piece front-end that hinged forward for access to the engine bay, a removable hardtop, knock-off aluminum wheels and a big-block 427. Chevrolet received overwhelming requests to have it produced.
The GS II (Grand Sport II) was a test vehicle completed in late 1963 by Chevrolet Engineering Center (C.E.C.). The chassis was constructed of spot-welded sheet steel and was fitted with narrow tires. With only minor testing done at GM’s test facility in Michigan, the vehicle was shipped to Texas to the Chaparral Cars test facility.
At Sebring in 1967, the Corvette L88 made its debut appearance. The L88 package included many competition components which included a M22 transmission, large disc brakes, upgraded suspension and an alumunim head 427. Shortly after the race, the L88 option would be offered on production cars which was a formidable package.
The Corvette built for 'Bunkie' Knudsen is a 1963 Chevrolet Corvette styling car known as the "Bunkie" Knudsen Corvette, built for Chevrolet general manager Semon E. "Bunkie" Knudsen. Finished in Rose Pearl with a full-length White racing stripe, it is outwardly distinguished by its chromed header-style pipes.
The "Asteroid" started life as a 1963 Chevy Corvette. It was ordered by mechanical engineer and renowned mid-century speed boat racer Bob Nordskog, sans any exterior paint save for a primer coat. Instead, the car was shipped directed to Barris Kustoms with instructions for Barris to transform the brand-new Corvette into a more radical version of itself.
The Corvette Rondine concept was built by Pinanfarina and introduced at the 1963 Paris Motor Show. The car started life as a 1963 split-window Corvette, which is all the more unusual because Chevrolet introduced the split-window coupe at the same time that Pinanfarina was introducing a custom-built Corvette based on that very same platform.
For the 1964 New York World's Fair, Bill Mitchell and his Styling team at the Tech Center customized a production Sting Ray under Shop Order #10361 with a variety of items that transformed the already impressive Corvette into a showpiece like no other. An opening was cut into the center of the car's hood exposing a polished fuel injection manifold with the Corvette crossed flags in its very center.
These Big Block cars would be the high-water mark of Corvette performance and refinement for the C2 series of cars. The 427/400hp L68 came standard from the factory with the Holley triple two-barrel carburetor arrangement called Tri-Power. Only 2101 Corvettes in 1967 received this rare engine option which was a $305.50 cost.
The L71 was Chevrolet’s most powerful engine in 1967 which replaced the big-block L71 from the previous year. Using it’s famous ‘Tri Power’ intake manifold was rated by the factory at 435 bhp. Costing $437.10, 3,754 Corvettes were made with the L71 options and they could not come with automatic transmissions nor air conditioning.
Bill Thomas had one goal in mind when he designed and produced the Cheetah: beat the Ford Cobra. 25 examples were produced until sadly, the factory burnt down. After the blaze, chevrolet pulled out of the project. The power to weight ratio was phenomenal (it was almost 500lbs lighter than the cobra!). The V8 was pushed back as far as possible leaving the engine almost in the center of the car. Some examples were tuned as high as 520HP.
The CERV II was entirely Zora’s car. The CERV II was conceived early in 1962 and developed over the next year, after the GS program was squashed. The car was built under Zora's direction between 1963-'64. Zora had it in mind to develop a separate line of racing Corvettes but the idea got terminated by management.
Those that have laid eyes on the Astro I will not soon forget it. This 1967 Chevrolet prototype featured sleek body lines that embodied the feel of a far more aggressively styled Mako Shark. Although the Astro I was built with the intent to aid in the study of aerodynamics, no official documentation has been uncovered as to the results of this testing.
Some of the iconic American sports car’s earliest forays into racing were snuffed out before they ever truly began. The 1963 Corvette Grand Sport, a Zora Arkus-Duntov designed rendition, of the C2 was staged for track domination, both at home and abroad.
When first introduced to the world by Pontiac in 1964, the car showed so much promise that Chevrolet (allegedly) put a swift end to its development to prevent its production from hindering the sales of the Corvette. Afterall, with the introduction of the 1963 Split-Window Corvette, Chevy was finally seeing an increase in sales, something lacking for most of the first-gen.
For competition, race customers had a range of options available to them including the N03 36-Gallon Fuel Tank, closer rear axle ratios and the C48 Heater/Defroster Delete (-100). Most cars equipped like this came with either L78 or the L84 with Ram-Jet Fuel Injection.
For competition, race customers had a range of options available to them including the N03 36-Gallon Fuel Tank, closer rear axle ratios and the C48 Heater/Defroster Delete (-100). Most cars equipped like this came with either L78 or the L84 with Ram-Jet Fuel Injection.
The XP-819 Corvette prototype was introduced in 1964 by Frank WInchell and Larry Shinoda as the first, experimental, rear-engine Corvette coupe. The XP-819 was developed in the mid-1960's as an engineering exercise to determine if a rear-engine platform was right for the Corvette program. During that time, Chevrolet was still under a racing ban.
The first Z06 was actually an option package first offered with the 1963 Corvette. The package was developed by Corvette's legendary lead engineer and racing advocate Z0ra Arkus-Duntov. The Z06 option was designed to allow consumers to bolster the 1963 "Split-Window" Corvettes performance and handling capabilities for use on the race track. Selecting regular production option (RPO) Z06 when ordering a Corvette resulted in a car equipped with some tasty options.
The L84 was the most powerful 327 available for the 1965 Corvette thanks to its Ram-Jet Fuel Injection which was an expensive $538 option. For competition, race customers had a range of options available to them including the N03 36-Gallon Fuel Tank, closer rear axle ratios and the C48 Heater/Defroster Delete (-100).
The L88 was a special option package developed under the direction of Zora Arkus-Duntov, director of GM’s performance division. First introduced in 1967, the L88 Corvette featured a highly modified version of Chevy’s 427-cubic-inch V-8 engine. Although this engine received a factory horsepower rating of 435, actual engine output was somewhere between 540 and 580 horsepower, giving the “stock” L88 enough power to run a quarter-mile in the high-11-second range!
To clothe the 1965 mid engine Corvette chassis, the designers at Styling Staff proposed a much more radical shape than Zora Arkus Duntov, the main force behind a mid engine Corvette, had in mind. It would have provided rear vision solely through a periscope. The design had bold air intakes at the rear and a split windscreen that lifted up with the gullwing doors.
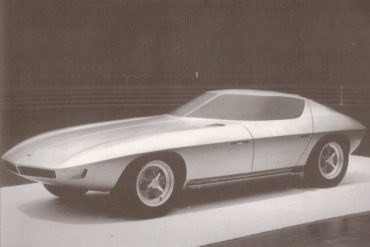
The 1963 Wedge Corvette split windshield concept was a sleek, front-engine design study that revived the Q Corvette’s split-windshield gullwing-style doors with a short, bobbed tail. Late in 1963, a GM Styling team under Henry Haga prepared this future Corvette proposal. Its sophisticated lines included side-mounted exhaust pipes.