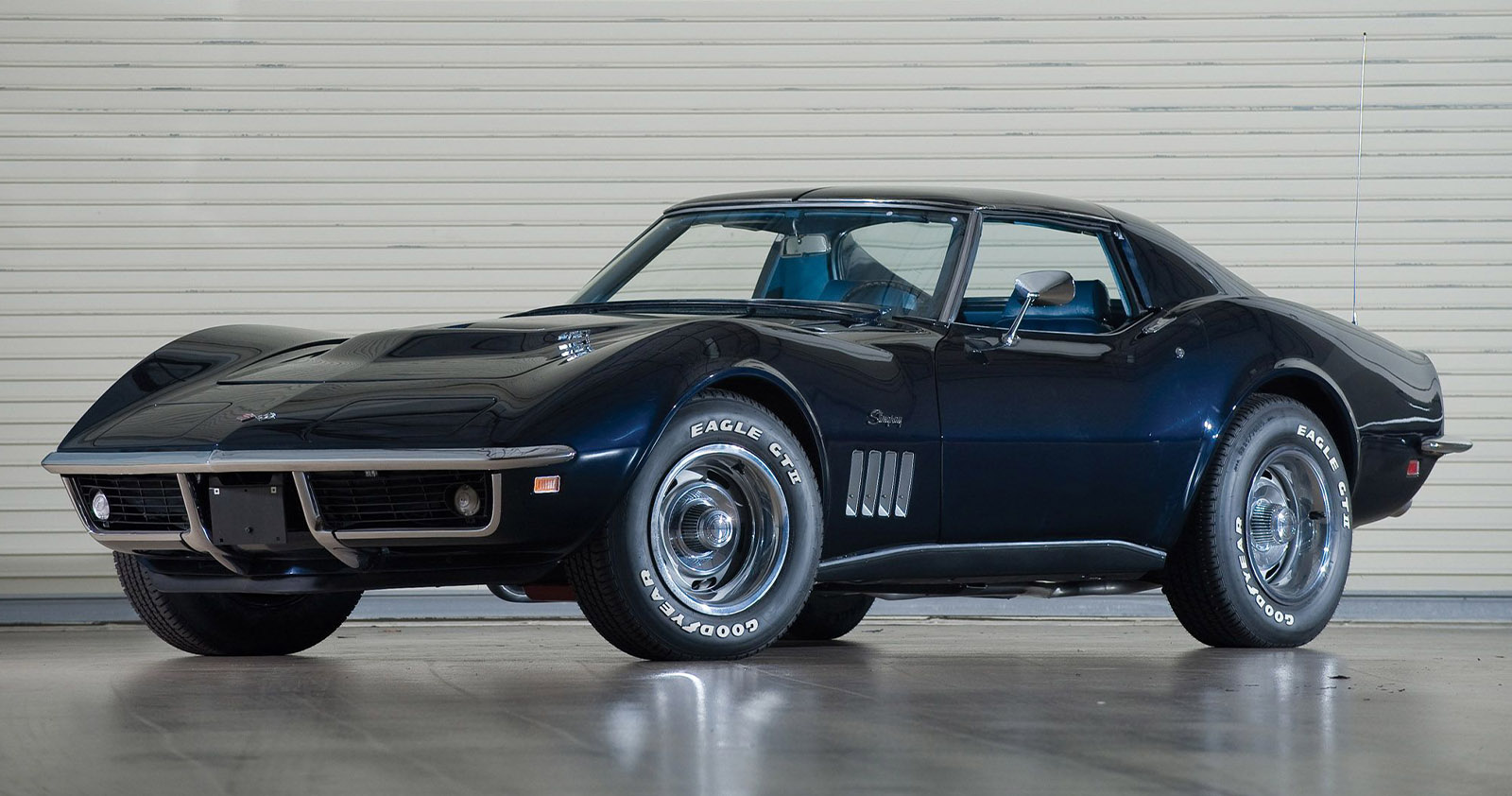
Just like about everyone else in our Corvette community, I am brimming with anticipation and excitement over the important stuff,...
The 1993 40th Anniversary ZR1 is widely regarded as one of the most sought-after Corvettes ever manufactured. Chevrolet meticulously crafted...
This beautiful 1990 ZR-1, listed on the duPont Registry and offered by Fusion Motor Company, popped up on my Facebook...
In 2018, the Indianapolis Motor Speedway made the Chevrolet Corvette the official pace car for the 102nd running of the...
Nowadays, the C7 Corvette ZR1 are seeing high prices in auction sites such as Bring A Trailer. After all, Chevy...
This is a 2019 Chevrolet Corvette ZR1 coupe finished in Torch Red over Jet Black leather and microsuede upholstery. It...
If you’ve been around the Internet on car forums for any amount of time you probably know the old joke,...
A unique Chevrolet Corvette ZR1 is currently being auctioned on Bring A Trailer. Dubbed the “Hero Edition ZR1,” this 2011...
The C6 Corvette’s ZR1 edition earned a reputation as a formidable adversary to supercars, despite not being officially classified as...
When it was released, the ZR-1 was a costly option that would transform conventional Corvettes into a sports car that...
Bring A Trailer is currently offering a gorgeous example of a 2019 Chevrolet Corvette ZR1 that comes with the optional...
Well, I must admit, that was quicker than I expected, as I just did a story on this last Tuesday....
My first impression after taking this nostalgic walk back to the supercars of the 90s was wow, look how far...
In this new video from YouTube channel, The Fast Lane Car, we get to see a 1990 C4 Chevy Corvette...
The 2019 Corvette ZR1 was developed with the intent of building a super-car iteration of the Corvette that pushed the limits of the brand...
Maybe my astute readers can help explain the psychology. Why are these kids and (gasp) grown adults still filming their...
Bring A Trailer is offering another 2019 Chevrolet Corvette ZR1 finished in Arctic White over a Jet Black upholstered and...
Another 2019 Corvette ZR1 is now on listed on Bring A Trailer and this one has only 250 miles on...
Although there was a lot of uncertainty about the Corvette’s long-term viability in its early days, the public’s perception of...
Bring A Trailer is proud to offer this all black 2019 Chevrolet Corvette ZR1 with just 4,300 miles on its...
Live now on Bring A Trailer is a 2010 Chevrolet Corvette ZR1 that boasts only 14k miles from new. The...
American tuning company Hennessey Performance Engineering specializes in making cars go faster. They offer a variety of performance packages that...
The 2019 Corvette ZR1 was developed with the intent of building a super-car iteration of the Corvette that pushed the limits of...
The Corvette and the Dodge Challenger are two of the best American sports cars and have a decades-long rivalry. Ever...
We want to share with you this 1990 Corvette ZR-1 that we found listed on Bring A Trailer. Normally we...
The 2019 Corvette ZR1 was developed with the intent of building a super-car iteration of the Corvette that pushed the limits of...
In 2010, for anyone that still needed more horsepower than even the Z06 could offer (and for anyone that could...
Today’s video is a footage that’s full of street racing action on the Florida highways. The protagonist is a supercharged...
Car and Driver’s Lightning Lap series is an annual test to see how new cars from different classes fare against...
The 2019 Corvette ZR1 was developed with the intent of building a super-car iteration of the Corvette that pushed the...